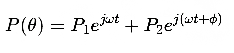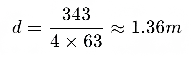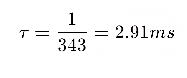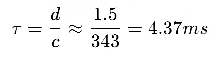Explore the World of Pro Audio
Cardioid Subwoofer Arrays: Optimizing Low-Frequency Control
Controlling low-frequency dispersion in professional sound systems is a key challenge in live events and fixed installations. Cardioid subwoofer arrays improve sound directivity by reducing energy radiated to the rear of the system while maximizing sound pressure for the audience. In this article, we will explore how to implement cardioid arrays using exclusively the Tecnare SW218V and SW218EB subwoofers, delving into their configuration, physical principles, and key mathematical formulations.
Physical Principles of Cardioid Subwoofer Arrays
Where:
- P is the resulting sound pressure at a given point.
- A1 and A2A are the amplitudes of the subwoofer waves.
- ϕ is the phase shift applied for cancellation.
- ω is the angular frequency of the wave.
When the sum of the waves is in phase at the front and out of phase at the rear, a cardioid pattern is achieved.
Cardioid Configurations with SW218V and SW218EB
1. Linear Configuration (Stacked End-Fire)
The End-Fire configuration uses subwoofers aligned in a row with progressive delays. The key principle is that the rear wave is canceled due to the phase difference introduced by the delay applied to each subwoofer.
Example with SW218V:
- Place three SW218V in a row, spaced at d = \frac{c}{4f}, where is the speed of sound (343 m/s) and is the central frequency of the array.
- Apply delays of T= d/c to the rear subwoofers to align the waves forward
- Invert the polarity of the last subwoofer to enhance rear cancellation.
Example Calculation: For a frequency of 63 Hz, the optimal spacing is:
Advantages:
- Effective rear cancellation.
- Increased subwoofer throw to the front.
2. Cardioid Block Configuration
This technique consists of stacking subwoofers in a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio (two facing forward and one facing backward), inverting the polarity and applying a delay to the rear subwoofer.
Example with SW218EB:
- Position two SW218EB facing forward and one oriented towards the rear.
- Invert the polarity of the rear subwoofer.
- Apply a delay of T= d/c ms to the rear subwoofer to synchronize the phase.
For a separation of 1 meter:
Advantages:
- Compact configuration.
- Reduces unwanted energy on stage or behind the system.
3. Circular Cardioid Array Configuration
In large-scale events, a circular array provides uniform dispersion with minimal rear emission.
Example with SW218V and SW218EB:
- Position four SW218EB forming a square, with two facing forward and two facing backward.
- Invert the polarity of the rear subwoofers.
- Apply delays to the rear subwoofers according to the formula:
4. Adjust the phase response using the Tecnare DP4896 processor.
Advantages:
- Ideal for 360° events or immersive setups.
- Minimizes subwoofer spill in unwanted areas.
Conclusion
Cardioid subwoofer arrays are essential for improving sound intelligibility and control in live events and indoor venues. While the SW218V allows for flexible configuration using phase and delay techniques, the SW218EB provides a more direct solution with its native cardioid design. With these Tecnare tools and a design based on physical principles and precise calculations, sound engineers can optimize coverage and minimize unwanted interference, achieving a more precise and efficient sound in any environment.