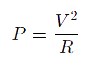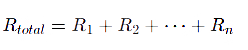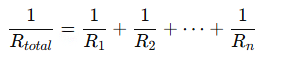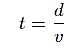Sound Equipment and Technologies
In the field of professional audio, using the right equipment and technologies is essential to achieve faithful, clear, and powerful sound reproduction. From speakers and amplifiers to signal processors and control software, each component plays a key role in sound quality. In this chapter, we will explore in detail the main equipment used in professional audio and the technologies that optimize their performance.
Audio Equipment and Technologies
Speakers and Sound Reinforcement Systems
Types of Speakers
Speakers can be classified according to their function and design as:
-
Full-Range: Reproduce the entire audible frequency spectrum.
-
Subwoofers: Designed for low frequencies, enhancing presence and impact in the bass range.
-
Line Array: Used in large events for their uniform dispersion and extended reach.
Example: Tecnare offers a wide range of speakers in each category, such as the E Series for full-range applications, the SW Series for subwoofers, and the Array Series for line array systems.
Difference Between Active and Passive Speakers
Active Speakers: Include built-in amplification and digital processing, simplifying installation and optimization.
Passive Speakers: Require external amplification and separate processing but offer greater flexibility in system design.
Power Handling
The power handling of a speaker is expressed in watts (W) and is classified as:
-
RMS Power: Continuous power the speaker can handle without damage.
-
Peak Power: Maximum power over short periods.
The power equation is:
Where:
-
P is the power in watts,
-
V is the applied voltage,
-
R is the speaker impedance.
Frequency Response
This is the range of frequencies a speaker can reproduce faithfully, expressed in Hz. A typical range for professional systems is 20 Hz – 20 kHz.
Impedance
A speaker’s impedance affects its interaction with the amplifier and is measured in ohms (Ω). Typical values are 4Ω, 8Ω, and 16Ω.
-
Series Connection:
- Parallel Connection:
Performance and Sensitivity
Sensitivity indicates how much sound pressure a speaker produces with 1 W of input, measured at 1 meter, expressed in dB SPL.
Distortion
Distortion occurs when the speaker introduces harmonics not present in the original signal. It is measured as THD (%).
Directivity
This is the speaker’s ability to project sound in a specific direction, described by polar patterns.
Maximum Sound Pressure Level
The maximum sound pressure level a speaker can generate is calculated with:
Where:
- SPL_{max} is the maximum level in dB SPL
- SPL_{1W/1m} is the sensitivity,
- P is the rated power in watts.
Power Amplifiers
Function and Types of Amplifiers
Amplifiers boost the audio signal to drive the speakers. They are classified as:
-
Class A/B: High fidelity but lower efficiency.
-
Class D: Higher efficiency and lower heat dissipation, ideal for high-power systems.
Example: Tecnare TDA Series or T Series use Class D technology to maximize performance with minimal energy loss.
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs)
What is a DSP?
A Digital Signal Processor allows real-time adjustments to the audio signal, including:
-
Parametric equalization
-
Protection limiters
-
Delay adjustment and phase alignment
Applications in Sound Systems
DSPs are used to optimize system response, preventing unwanted cancellations and boosts. The delay calculation equation is:
Where:
-
d is the distance in meters,
-
v is the speed of sound (~343 m/s at 20°C).
Example: Tecnare TDAP Series incorporates advanced DSPs with configurable presets.
Control and Simulation Software
Acoustic Simulation
Tools like EASE Focus allow predicting system coverage and behavior before installation. Tecnare offers free simulations to optimize project design.
Remote Control and Monitoring
Modern systems include monitoring software to adjust and supervise parameters in real time, ensuring optimal performance.
Practical Case: Designing a Professional System
Suppose a sound system is designed for an auditorium with:
-
8 Tecnare CLA312 speakers in a line array configuration
-
4 Tecnare SW218V subwoofers
-
Amplification with Tecnare TDA Series and DSP processing
Setup Procedure:
-
Coverage Calculation: Determine the best placement and angling of the line array.
-
Phase and Delay Adjustment: Synchronize subwoofers with main speakers using DSP.
-
Equalization and Testing: Apply filters and perform measurements at different points in the venue.
Conclusion
The proper combination of equipment and technologies is key to achieving high-quality professional sound. From selecting speakers and amplifiers to configuring DSPs and control software, every detail influences the final result. If you want to optimize your Tecnare system, our team of engineers is available to advise you and provide personalized simulations. Contact us and take your installation to the next level!
Featured Articles
Tecnare
Loudspeakers Series
E Series
IBZA Series
V Series
ALIS Series
Array Series
SW Series
KT Series
TANIT Series
CS Series
Amplifiers Series
Digital Processors
Accessories